Postgres For Mac
Introduction
If you’re planning to run PostgreSQL on a Mac, it’s important to know how to install it properly. There are three common ways to install Postgres on a Mac: using Homebrew’s brew install command, downloading the DMG interactive installer for Postgres.app or using MacPorts. In this article, we’ll provide step-by-step instruction for all three of these methods, so you can choose the installation process that works best for you.
Prerequisites
Before attempting the instructions provided in this tutorial, make sure your Mac is running a supported version of MacOS X with at least 256MB of free disk space.
Hi I am having trouble with postgres. I don't remember my postgres password and don't know how to change the password. I'm guessing I should change the md5 password settings I set a month ago, but I don't know how to find the file and open it using my terminal. Disaat Anda ingin memainkan permainan DominoQQ, maka hal yang harus Anda lakukan pastinya dengan memilih situs domino yang telah resmi atau pun yang sudah dikenal oleh banyak orang agar tidak terjadi hal – hal buruk kepada Anda dan salah satu ciri – ciri yang paling menonjol dari suatu situs judi yang resmi itu adalah pada live chat yang disediakan.
Summary: in this tutorial, you will learn how to download the PostgreSQL, install PostgreSQL on macOS, and restore the sample database. Download PostgreSQL installer for macOS. To download the PostgreSQL installer, you follow these steps: First, visit the PostgreSQL installer download page.; Then, download the PostgreSQL for macOS.
Install PostgreSQL on a Mac
As we mentioned earlier, there are three common ways to install PostgreSQL on macOS. You can use a downloadable DMG installer from Postgres.app, a Homebrew repository for Postgres or a MacPorts installation that uses the port command line interface.
It’s also possible to build a binary of PostgreSQL from source using a tarball archive or to run Postgres in a Docker container; however, we won’t be providing instructions for these alternatives in this article.
Install Postgres using the Postgres.app
The easiest way to install Postgres on a Mac is to visit the Postgres.app downloads page and get the latest stable version of PostgreSQL as a DMG interactive installer.
Once the download is complete, navigate to your Downloads directory in a Finder window and then double-click on the DMG file to mount the installer. After mounting it, you should see a window pop up that will allow you to drag and drop the Postgres.app to your Applications folder.
Once you complete the installation steps, you should be able to run PostgreSQL by double-clicking the app’s icon in the Applications folder. You can also choose to have Postgres.app run by default– just add the application to your Login Items list in System Preferences.
Use the following export command in a macOS Terminal window to add the Postgres.app path to your current PATH environment variable:
export PATH='/Applications/Postgres.app/Contents/Versions/11/bin:$PATH' |
Install PostgreSQL using Homebrew
If you’d prefer to use Homebrew to install Postgres, you can do so using the brew install command. You’ll need to install the latest version of Homebrew using Ruby if you haven’t already. To do this, use the following command:
/usr/bin/ruby -e'$(curl -fsSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Homebrew/install/master/install)' |
If you’re running the latest Catalina version of macOS, the output of this command should look like the following:
> This script will install: /usr/local/bin/brew /usr/local/share/doc/homebrew /usr/local/share/man/man1/brew.1 /usr/local/share/zsh/site-functions/_brew /usr/local/etc/bash_completion.d/brew /usr/local/Homebrew |
It may take a few minutes to install Homebrew depending on your internet connection. When the installation is complete, the next step is to “doctor” the Homebrew installation and update its repositories with this compound command:
NOTE: The latest versions of Homebrew will update the repository before installing packages.
Mac install of Postgres using ‘brew’
Now that we’ve installed the latest version of Homebrew, we can use the brew install command to install PostgreSQL:
brew install postgresql |
NOTE: In Homebrew, the postgres “keg” is simply an alias for postgresql, so brew install postgres will work the same way.
Once the installation is finished, you can use the postgres -V or psql -V commands to return the version number and verify that the installation was successful. You can also use the brew list command to view a list of all locally installed packages using Homebrew.
psql command not found
If you get an error stating psql: command not found, you may have to export the path for the Homebrew installation using the following command:
As an alternative, you can also add the following PATH line to your ~/.bash_profile, ~/.bashrc or ~/.zprofile file:
PATH='/Library/PostgreSQL/11/bin:$PATH' |
After editing any of these files, be sure to save the changes. You can have the new settings take effect by running the source command followed by the file name:
Try executing the psql command again after making these changes to verify that the PATH for PostgreSQL and psql has been set.
Start the Postgres server
With Homebrew, you can use the brew services start command to have Postgres start in the background:
brew services start postgresql |
If you’d prefer to run Postgres as a temporary background service, use the following pg_ctl command instead:
You can use Homebrew’s enable command to have PostgreSQL start automatically whenever you restart your Mac:
brew services enable postgresql |
Reinstall PostgreSQL using Homebrew
If you already have PostgreSQL on your Mac and you’d like to reinstall the latest version of it, you can also use Homebrew’s reinstall command:
Install Postgres using MacPorts
The last method we’ll discuss in this article involves using the MacPorts package manager for macOS. To install Postgres on a Mac this way, visit the release page for MacPorts and download a .pkg installer that matches your version of macOS. Once the download is complete, you can navigate to your Downloads directory in a Finder window and double-click the package installer. Follow the steps for the interactive installer, and open a terminal window when you’re done.
NOTE: MacPorts also requires the Xcode library.
In order to install a package, you’ll need to export a path for Macport’s port command. Execute the following export command in a terminal window:
exportPATH=/opt/local/bin:/opt/local/sbin:$PATH /opt/local/bin |
You can also open your .bash_profile or .zprofile file and append the following:
After saving your changes to the file, go back to your terminal and input source ~/.bash_profile or source ~/.zprofile to load the changes.
Use Macport’s ‘port’ command to install Postgres
At this point, we’re ready to use the port command to install Postgres. Use the following port info command to look for the PostgreSQL package:
port info postgresql_select |
You should receive a response that looks like the following:
Now, use the port install command with sudo to install the PostgreSQL packages with elevated privilages:
sudo port install postgresql11 postgresql11-server |
NOTE: You’ll need to press return or type y to verify that you’d like to install the package and its dependencies.
Finally, use the select command shown below to verify that PostgreSQL installed correctly:
If you’re in the MacPort interface, you can just type q to quit.
Uninstall Postgres on a Mac
If you need to uninstall a Homebrew installation of PostgreSQL, use the following command to force the uninstall, even if it depends on other packages:
brew uninstall --ignore-dependencies postgresql |
If you’d like to see any existing PostgreSQL dependencies, use the command shown below:
Uninstall Postgres.app on a Mac
You can uninstall the Postgres.app installation of PostgreSQL the same way you would for any package or applicaton on a Mac– just drag and drop the application from the Applications folder to the Trash directory. Make sure to first shut down the Postgres application and server before attempting this.
Uninstall the MacPorts installation of Postgres
If you installed Postgres using MacPorts, you’ll need to use the following command to remove the package: Microsoft office 2016 free download windows 10.
sudo port uninstall postgres |
Conclusion
If you need to install PostgreSQL on a Mac, it’s good to know the different methods that are available. In this article, we provided instructions on three common installation methods: using the Homebrew package manager, using the interactive installer and using MacPorts. With this tutorial to guide you, you’ll be able to select any of these methods for your own PostgreSQL installation.
Postgres.app is a full-featured PostgreSQL installation packaged as a standard Mac app.It includes everything you need to get started:we’ve even included popular extensions like PostGIS for geo data and plv8 for JavaScript.
Postgres.app has a beautiful user interface and a convenient menu bar item.You never need to touch the command line to use it – but of course we do include all the necessary command line tools and header files for advanced users.
Postgres.app can install minor updates automatically, so you get bugfixes as soon as possible.
Installing Postgres.app
Download ➜ Move to Applications folder ➜ Double Click
If you don't move Postgres.app to the Applications folder, you will see a warning about an unidentified developer and won't be able to open it.
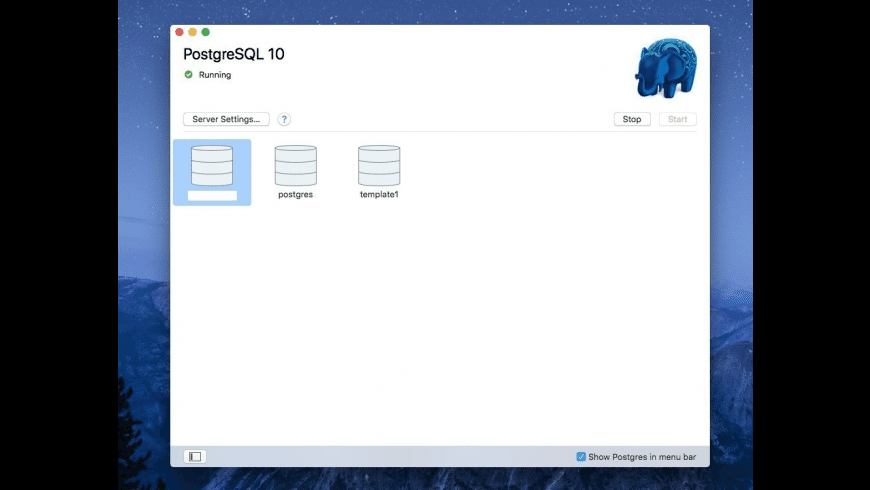
Utorrent for mac os download. Click 'Initialize' to create a new server
Configure your $PATH to use the included command line tools (optional):
Done! You now have a PostgreSQL server running on your Mac with these default settings:
| Host | localhost |
| Port | 5432 |
| User | your system user name |
| Database | same as user |
| Password | none |
| Connection URL | postgresql://localhost |
To connect with psql, double click a database. To connect directly from the command line, type psql. If you’d rather use a graphical client, see below.
NOTE: These instructions assume that you’ve never installed PostgreSQL on your Mac before.If you have previously installed PostgreSQL using homebrew, MacPorts, the EnterpriseDB installer, consider removing other PostgreSQL installations first.We also have instructions for upgrading from older versions of Postgres.app.
Graphical Clients
Postgres App For Mac
Postgres.app includes psql, a versatile command line client for PostgreSQL.But it’s not the only option; there are plenty of great graphical clients available for PostgreSQL.Two popular tools are:
pgAdmin 4 is a feature rich open source PostgreSQL client.It has support for almost every feature in PostgreSQL.The only downside is that the cross-plattform UI really doesn’t live up to the expectations of a native Mac app.
Postico on the other hand, is a very modern Mac app.It’s made by the same people that maintain Postgres.app, and we think you’ll like it! We put a lot of effort into making it a joy to use.However, it doesn’t have the extensive feature set of pgAdmin, and it’s a commercial app rather than open source.
Aside from those two options, there are a lot more to choose from! Check the documentation for a list of amazing Mac apps for PostgreSQL.
How to connect
After your PostgreSQL server is up and running, you’ll probably want to connect to it from your application.Here’s how to connect to PostgreSQL from popular programming languages and frameworks:
To connect from PHP, make sure that it supports PostgreSQL. The version included with macOS doesn't support PostgreSQL. We recommend MAMP for an easy way to install a current version of PHP that works.
You can use PDO (object oriented):
Or the pg_connect() functions (procedural):
To connect to a PostgreSQL server with Python, please first install the psycopg2 library:
Django
In your settings.py, add an entry to your DATABASES setting:
Flask
When using the Flask-SQLAlchemy extension you can add to your application code:
SQLAlchemy
To install the pg gem, make sure you have set up your $PATH correctly (see Command-Line Tools), then execute the following command:
Rails
In config/database.yml, use the following settings:
Sinatra
In config.ru or your application code:
ActiveRecord
Install the activerecord gem and require 'active_record', and establish a database connection:
DataMapper
Install and require the datamapper and do_postgres gems, and create a database connection:
Sequel
Install and require the sequel gem, and create a database connection:
- Download and install the PostgreSQL JDBC driver
- Connect to the JDBC URL jdbc:postgresql://localhost
For more information see the official PostgreSQL JDBC documentation.
Postgres For Mac
libpq is the native C client library for connecting to PostgreSQL. It's really easy to use:
Now compile the file with clang and run it:
You can just use the C API in Swift! First include libpq in your bridging header:
Then make sure to link with libpq.
On iOS, you'll need to build libpq yourself.
Postgresql Download For Mac
On macOS you can use the system provided libpq (does not support SSL) or use libpq provided by Postgres.app by adding the following build settings:
| Other Linker Flags | -lpq |
|---|---|
| Header Search Paths | /Applications/Postgres.app/Contents/Versions/latest/include |
| Library Search Paths | /Applications/Postgres.app/Contents/Versions/latest/lib |
Postgres Client For Mac
Now you can use the libpq C library to connect to PostgreSQL:
Support
We have a list of common problems in the troubleshooting section in the documentation.
For general questions concerning PostgreSQL, have a look at the official PostgreSQL documentation.
If you have a question concerning Postgres.app that is not answered by the Postgres.app documentation,you can ask @PostgresApp on Twitter, or open an issue on GitHub.
When reporting bugs, let us know which version of Postgres.app & macOS you are using, and be sure to include detailed error messages, even if your issue seems similar to another one.
Postgres Driver For Mac
License
Postgres.app, PostgreSQL, and its extensions are released under the PostgreSQL License. The released binaries also include OpenSSL (OpenSSL License), PostGIS (GPLv2), and plv8 (3 clause BSD).
Postgres Mac Client
Postgres.app is maintained by Jakob Egger. It was originally created by Mattt Thompson.